Humans process cannabis because we have a built in system of receptors already in place. Humans produce endogenous cannabinoids naturally – anandamide and 2-arachidonoyl glycerol (2AG). The body has cannabinoid receptor sites throughout that not only react to endogenous cannabinoids but to phytocannabinoids such as cannabis.
Discovery of Endocannabinoid System: ECS
Dr. Raphael Mechoulam, also known as the "father of cannabis", is an Israeli organic chemist and a professor of Medicinal Chemistry at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem in Israel.
Mechoulam is best known for his work (together with Y. Gaoni) in the isolation, structure elucidation and total synthesis of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol.
The main active principle of cannabis and for the isolation and the identification of the endogenous cannabinoids anandamide from the brain and 2-arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) from peripheral organs together with his students, postdocs and collaborators.
Professor Allyn Howlett, working with Mechoulam, was a young researcher in St. Louis. She got DEA approval for her research, and she found a receptor site in the brain for THC and named it CB1.
This was a major discovery. It was the first indication that there were cannabinoid receptors in the human body - but why? You may be familiar with anandamide if you're, say, a runner and have experienced the wave of euphoria after a successful jog, commonly known as "runner's high."
A neurotransmitter produced in the brain that binds to THC receptors. It's called the "bliss molecule" Ananda, which is sanskrit work for joy or bliss.
Raphael Mechoulam's major scientific interest is the chemistry and pharmacology of cannabinoids.
He and his research group succeeded in the total synthesis of the major plant cannabinoids Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol, cannabigerol and various others.
Another research project initiated by him led to the isolation of the first described endocannabinoid - anandamide, which was isolated and characterized by two of his postdoctoral researchers, Lumír Ondřej Hanuš and William Devane. Another endogenous cannabinoid, 2-AG, was soon discovered by Shimon Ben-Shabat, one of his PhD students.

What Are Cannabinoid Receptors?
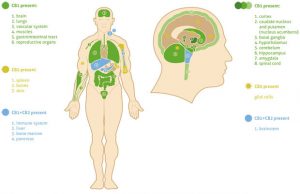
Cannabinoid receptors are present throughout the body and are embedded in cell membranes. They're believed to be more numerous than any other receptor system.
CB1 receptors are predominantly found in the brain, nervous system, connective tissues, gonads, glands and organs.
On the other hand, CB2 receptors are predominantly found in the immune system. The vast diversity of the receptor locations shows just how important endocannabinoids are for day-to-day bodily function.
Endocannabinoids help regulate the following things: Sleep, appetite, digestion, hunger, mood, motor control, immune function, reproduction and fertility, pleasure and reward, pain, memory, and temperature regulation.
Endocannabinoids are the chemical messengers that tell your body to get these processes moving and when to stop them. They help maintain optimal balance in the body, which is a process that's also known as homeostasis. When the ECS is disrupted, any one of these things can fall out of balance.
Where Do Endocannabinoids Come From?
If your body cannot produce enough endocannabinoids, you might be in for some trouble. But, where do endocannabinoids come from, anyway?
This question has another simple answer: diet. Your body creates endocannabinoids with the help of fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids are especially important for this.
Recent research in animal models has found a connection between diets low in omega-3s and mood changes caused by poor endocannabinoid regulation.
Hemp seeds are a quality source of omgea-3s as are fish, such as salmon and sardines.
© 2018 Massage Topicals

